Knee Replacement
This page contains information about total knee replacement. You should contact your GP or health professional if you have any questions about the procedure.
Arthritis explained
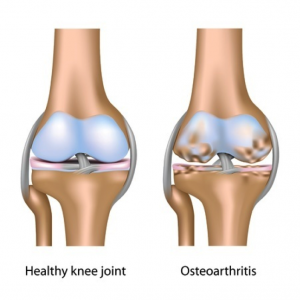
Arthritis is a collection of conditions. It can cause damage to one or more joints.
Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis, resulting in the gradual wear and tear of joints.
Inflammation of the joints is associated with some types of arthritis.
Arthritis causes pain and stiffness in the joint as it eventually wears away the normal cartilage covering the surface of the joint. The bone underneath then becomes damaged.
The benefits of surgery
A successful knee replacement should result in less pain and walking should be easier.
Alternatives to a total knee replacement
Anti-inflammatory painkillers (ibuprofen) and painkillers such as paracetamol can help control the pain.
Including supplements in your diet may also help to alleviate symptoms, but you should always check with your GP before taking them.
An elastic support worn around the knee can increase the feeling of stability and a walking stick can aid walking.
Moderate exercise on a regular basis can help to lessen stiffness in your knee.
Pain and stiffness can sometimes be reduced by a steroid injection into the knee joint.
As your arthritis worsens, these measures will become less effective.
Patello-femoral and unicompartmental knee replacements are partial knee replacements which are available for patients with osteoarthritis that is limited to just one part of the knee.
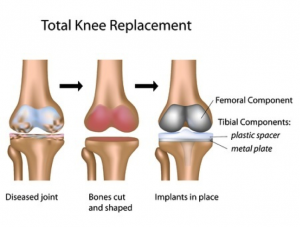
What the operation entails
The operation usually takes between an hour and an hour and a half and many anaesthetic techniques are possible.
Your surgeon will remove the damaged joint surfaces via a cut on the front of your knee. They will be replaced with an artificial knee joint. This is made from metal, plastic or a combination of the two.
Complications
General
• Pain
• Blood clots
• Scarring
• Bleeding
• Infection of the surgical wound site
• Chest infection
• Heart attack
• Stroke
• Difficulty passing urine
Specific
• Dislocation
• Continued discomfort in the knee
• Damage to nerves
• Infection in the knee
• Damage to blood vessels
• Mechanical loosening of the knee implant
• Damage to ligaments or tendons
• Sever pain, stiffness and loss of use of the knee (complex regional pain syndrome)
Recovery time
You can usually go home three to seven days after the procedure.
You will require walking sticks or crutches for several weeks.
You should be able to return to normal activities following regular exercise. However, ask your GP or health care professional for advice before you start exercising.
Generally most people make a good recovery, experience less pain and find it easier to get around.
As an artificial knee is never quite the same as a normal knee; kneeling down is not recommended and is usually uncomfortable.
You may find that your knee replacement wears out with time.
Total knee replacement summary
Occasionally, arthritis of the knee is the result of rheumatoid arthritis or a previous knee injury.
Arthritis generally occurs without a known cause. A knee replacement should reduce your pain and help you walk more easily if you suffer severe pain, stiffness and disability due to arthritis.
We look forward to hearing from you to discuss your needs and see how we can get you the best treatment, quickly and affordably.
Please contact us for further information about treatments not listed here

